Flutter has rapidly become one of the most popular frameworks for building beautiful, cross-platform mobile apps. Backed by Google, it allows developers to write a single codebase and deploy it seamlessly to Android, iOS, web, and even desktop.
Flutter simplifies cross-platform app development with its fast reload, expressive UI, and single codebase.
What is Flutter?
Flutter is an open-source UI toolkit built by Google. It enables developers to create natively compiled applications using Dart, Google’s programming language optimized for UI development.
With Flutter, you can:
• Build apps for Android, iOS, web, and desktop from one codebase.
• Achieve native performance using Flutter’s own rendering engine.
• Use hot reload to instantly see code changes.
• Create beautiful UIs with Material Design and Cupertino widgets.
Step 1: Setting Up Your Development Environment
1. Install Flutter SDK
Visit the official Flutter website and download the SDK for your OS (Windows, macOS, or Linux). Run:
- flutter doctor
This checks your environment and shows missing components like Android Studio or Xcode.
2. Install an IDE
Recommended IDEs:
• Android Studio
• VS Code
• IntelliJ IDEA
Add Flutter and Dart plugins from the marketplace.
Step 2: Creating Your First Flutter Project
Run the following commands:
flutter create hello_flutter
cd hello_flutter
flutter run
This launches your first working Flutter app.
Step 3: Understanding Flutter’s Structure
A typical Flutter app follows a widget tree. Everything in Flutter is a widget.
Example:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Hello Flutter',
theme: ThemeData(primarySwatch: Colors.blue),
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('Welcome to Flutter')),
body: const Center(child: Text('Hello World')),
),
);
}
}
Flutter UI : Core widgets
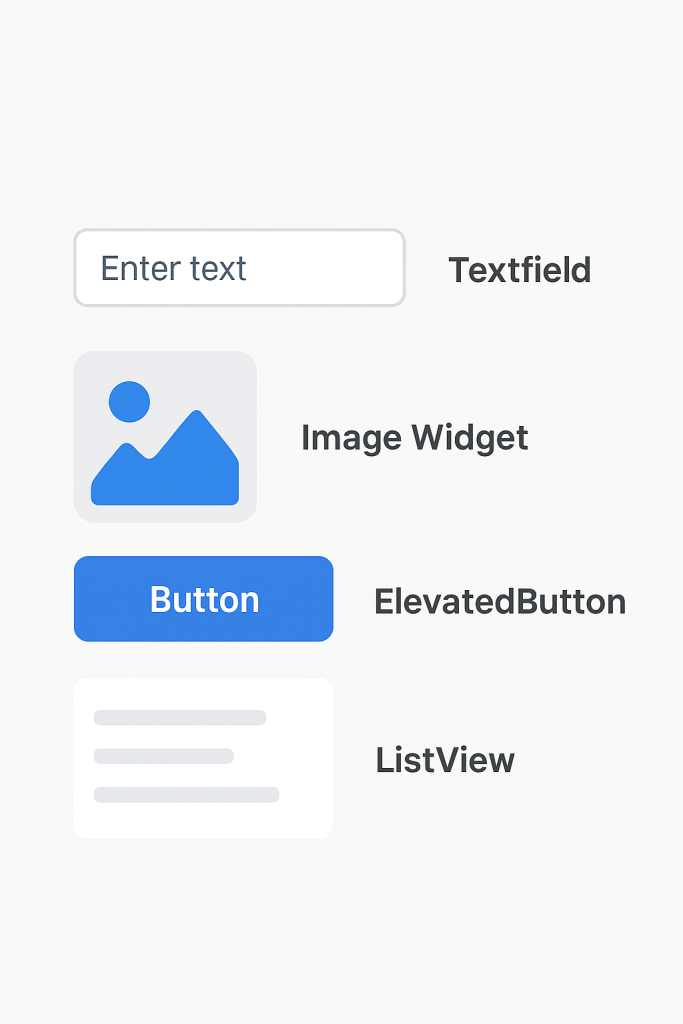
Text and Styling:
Text(
'Welcome to Flutter!',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 24,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.teal,
letterSpacing: 1.2,
),
);
Image Widgets :
Image.asset('assets/images/logo.png');
Image.network('https://example.com/image.png');
# Use local (assets/) or network images. Declare asset paths in pubspec.yaml.
flutter:
assets:
- assets/images/logo.png
- assets/images/banner.jpg
Buttons :
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {},
child: Text('Submit'),
);
TextButton(onPressed: () {}, child: Text('Cancel'));
IconButton(icon: Icon(Icons.favorite), onPressed: () {});
Buttons come in multiple styles: ElevatedButton, OutlinedButton, TextButton
Input Fields :
TextField(
decoration: InputDecoration(
labelText: 'Email',
prefixIcon: Icon(Icons.email),
border: OutlineInputBorder(),
),
);Lists and Scrolling :
Use ListView, GridView, or SingleChildScrollView for scrolling content.
ListView.builder(
itemCount: items.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
return ListTile(
leading: Icon(Icons.person),
title: Text(items[index]),
);
},
);Next, we’ll explore layout widgets, navigation, dialogs, state management, and deploying an app.









