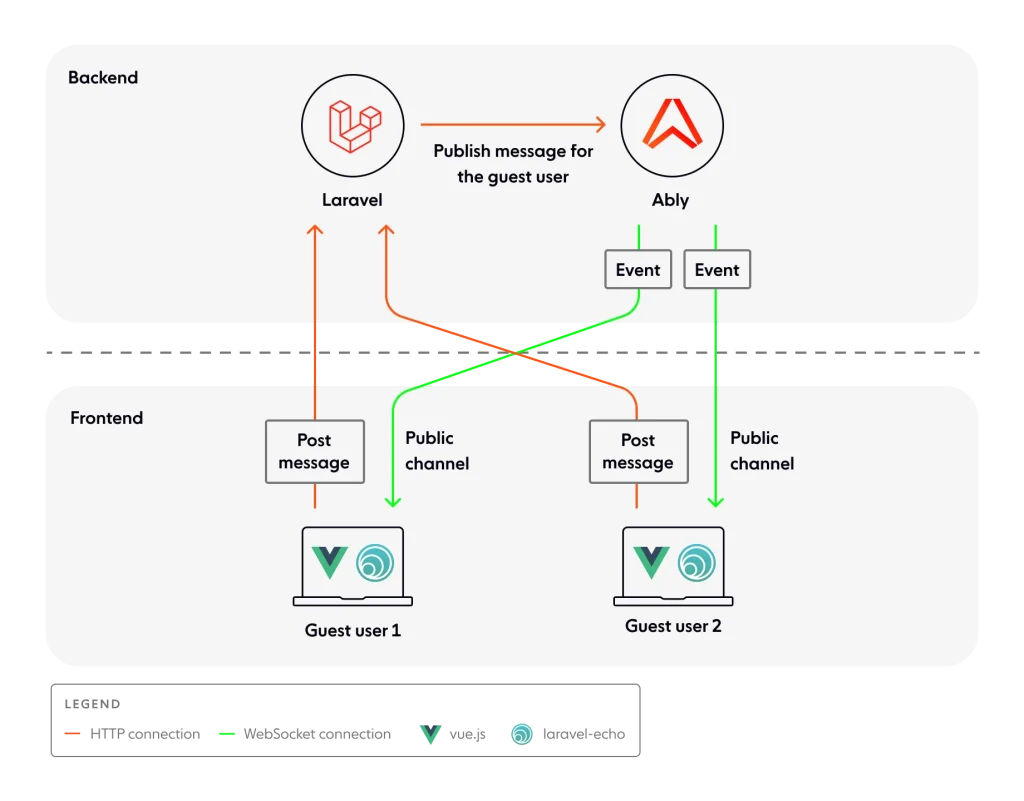
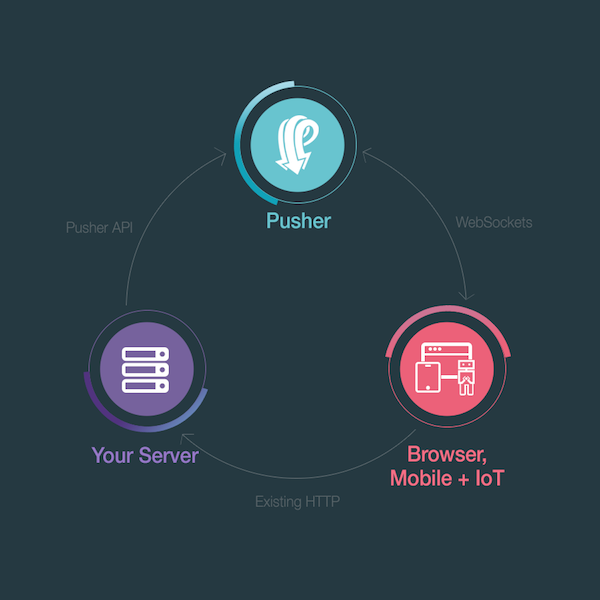
In today’s web applications, users expect instant updates — whether it’s a new message, order status change, comment, or system alert. Real-time notifications improve engagement, user experience, and responsiveness.
In this blog, we’ll learn how to build a real-time notification system in Laravel using:
- Laravel Broadcasting
- WebSockets
- Pusher
- Events & Notifications
Let’s break it down in a simple and practical way.
What is Real-Time Broadcasting?
Normally, browsers request data from the server (HTTP request → response).
In real-time systems, the server pushes data automatically to users without refreshing the page.
Laravel makes this easy using:
- Events – Something that happens (e.g., OrderPlaced)
- Broadcasting – Sending that event to the frontend
- WebSockets – Persistent connection for instant communication
- Pusher – A hosted WebSocket service
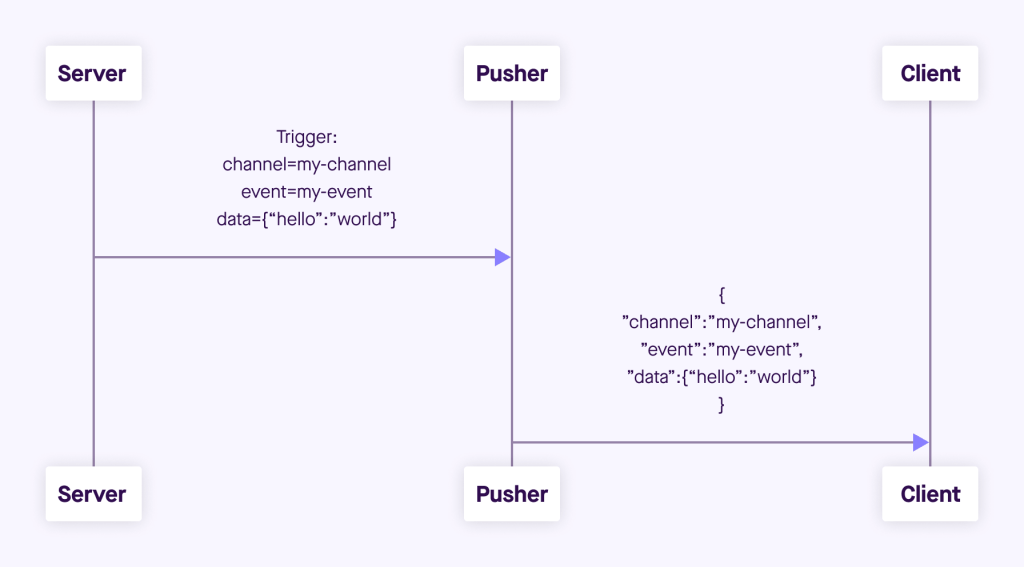
Step-by-Step Flow:
- User performs an action (e.g., places an order)
- Laravel fires an Event (
OrderPlaced) - Event implements
ShouldBroadcast - Laravel sends the event to Pusher
- Pusher pushes data via WebSockets
- Frontend (Laravel Echo + JS) listens and updates UI instantly
No refresh. No polling. Pure real-time.
Step-by-Step Implementation
1️⃣ Install Broadcasting Dependencies
composer require pusher/pusher-php-server
npm install --save laravel-echo pusher-js2️⃣ Configure Broadcasting
In .env:
BROADCAST_DRIVER=pusher
PUSHER_APP_ID=your_id
PUSHER_APP_KEY=your_key
PUSHER_APP_SECRET=your_secret
PUSHER_APP_CLUSTER=mt1In config/broadcasting.php, ensure Pusher is configured.
3️⃣ Create an Event
php artisan make:event OrderPlacedUpdate the event:
use Illuminate\Contracts\Broadcasting\ShouldBroadcast;
class OrderPlaced implements ShouldBroadcast
{
public $order;
public function __construct($order)
{
$this->order = $order;
}
public function broadcastOn()
{
return ['orders'];
}
}Now when this event is fired, it will broadcast automatically.
4️⃣ Fire the Event
event(new OrderPlaced($order));That’s it — Laravel handles the rest.
5️⃣ Setup Laravel Echo (Frontend)
In resources/js/bootstrap.js:
import Echo from 'laravel-echo';
import Pusher from 'pusher-js';
window.Pusher = Pusher;
window.Echo = new Echo({
broadcaster: 'pusher',
key: import.meta.env.VITE_PUSHER_APP_KEY,
cluster: import.meta.env.VITE_PUSHER_APP_CLUSTER,
forceTLS: true
});Listen for events:
Echo.channel('orders')
.listen('OrderPlaced', (e) => {
console.log('New order:', e.order);
});Now your UI updates instantly.
Public vs Private vs Presence Channels
Laravel supports three types of channels:
| Channel Type | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Public | Anyone can listen |
| Private | Authenticated users only |
| Presence | Shows who is online |
Example of private channel:
return new PrivateChannel('orders.' . $user->id);Using Laravel Notifications (Optional but Powerful)
Instead of manually firing events, you can use Laravel’s built-in Notification system.
php artisan make:notification OrderNotificationIn notification:
public function via($notifiable)
{
return ['broadcast'];
}Laravel will automatically handle broadcasting.
Why Use Pusher?
Pusher removes the complexity of:
- Managing WebSocket servers
- Scaling connections
- Handling reconnections
- SSL security
It’s fast, reliable, and easy to integrate.
Alternative: Laravel WebSockets (Self-Hosted)
If you don’t want third-party services:
You can use:
- beyondcode/laravel-websockets
This allows you to run your own WebSocket server.
Best for:
- Large scale apps
- Cost control
- Full infrastructure ownership
Real-Time vs Traditional Polling
| Feature | Polling | Broadcasting |
|---|
| Speed | Slower | Instant |
| Server Load | High | Efficient |
| User Experience | Medium | Excellent |
| Scalability | Limited | High |
Best Practices
✔ Use queues for broadcasting in production
✔ Secure private channels
✔ Use presence channels for chat apps
✔ Optimize event payload (don’t send large data)
✔ Handle reconnection on frontend
Real-World Use Cases
- Chat applications
- Live order tracking
- Admin dashboards
- Stock price updates
- Social media notifications
- Multiplayer games
Final Thoughts
Laravel makes real-time applications surprisingly simple.
With:
- Events
- Broadcasting
- WebSockets
- Pusher
You can build powerful notification systems with minimal effort.
Real-time features are no longer optional — they are expected.
If you’re building modern applications, mastering Laravel Broadcasting is a must.









